$11,500,000 USD

786-245-1165
OVERVIEW
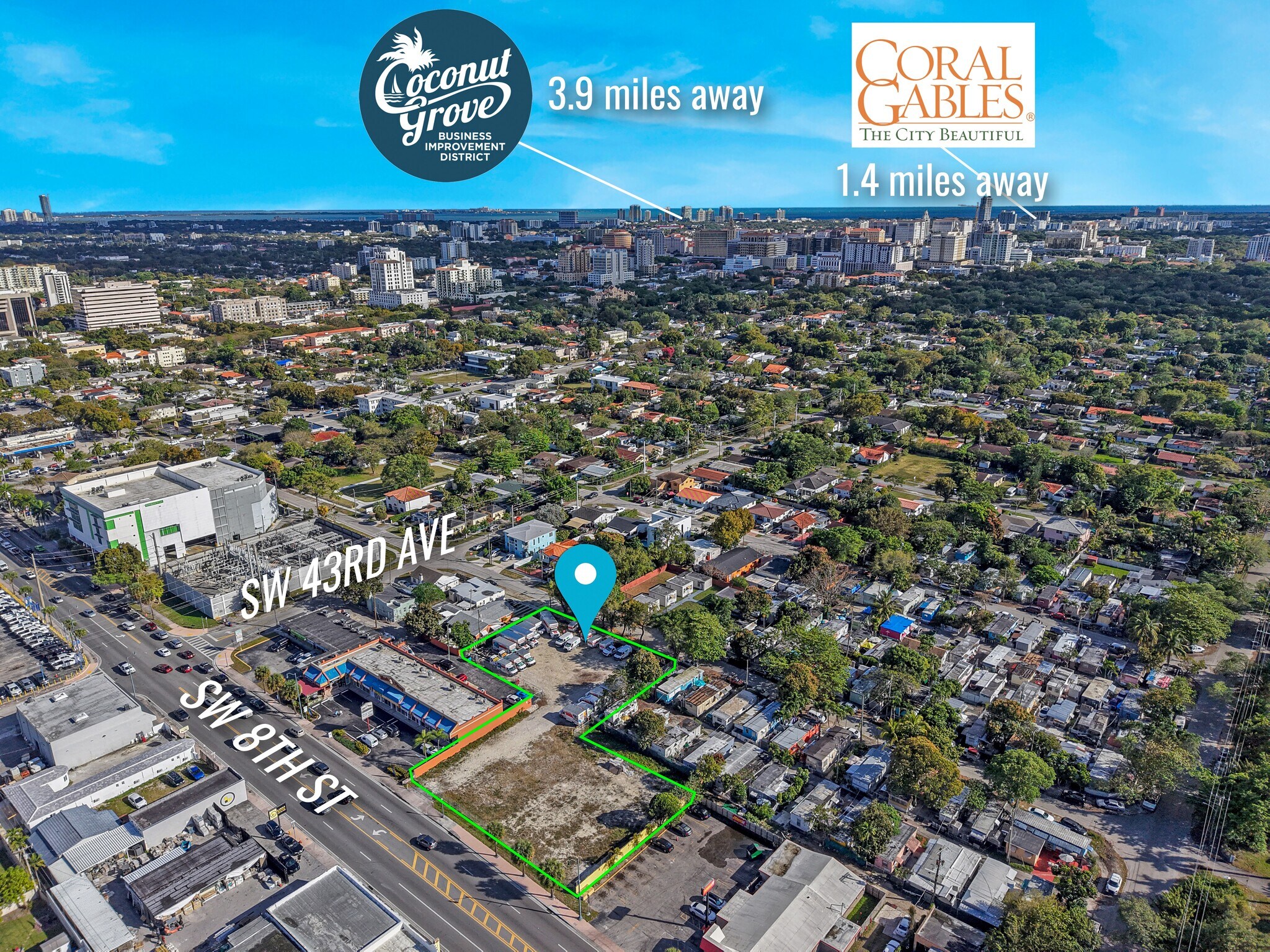
Lot #1 closer to 8th St
BU-3B zoning district in Miami generally refers to Business District zoning that allows for a variety of commercial and mixed-use developments. Under the BU-3B zoning code, here's a breakdown of what you might be able to build:
1. Commercial and Retail Uses
Retail stores (e.g., clothing, grocery, and specialty stores).
Personal service establishments (e.g., beauty salons, dry cleaners, etc.).
Offices (e.g., professional, medical, or administrative offices).
Restaurants and cafes.
Banks and financial institutions.
2. Mixed-Use Developments
You may also develop properties with both commercial and residential uses. For example, you could have ground-floor retail and office spaces, with apartments or condominiums on the upper floors.
3. Commercial/Residential Buildings
Hotels or motels.
Multifamily residential buildings, such as apartments or condominiums, as long as they are part of a mixed-use project.
4. Parking Lots and Structures
Parking lots, garages, and structures are typically allowed to support the commercial use of the property.
5. Other Conditional Uses
Some uses may require a special permit or conditional use approval, such as:
Light manufacturing or assembly (typically non-polluting).
Cultural or recreational uses (e.g., art galleries, fitness centers).
Restrictions
Height and density limits: These depend on the exact location and the specific neighborhood plan. There may be restrictions on how tall or dense you can build.
Setback requirements: These will dictate how far from the street, property lines, or adjacent buildings you must build.
Parking requirements: Depending on the size and type of development, there may be minimum parking space requirements.
Lot #2
BU-2 (Business, General) zoning designation in Miami, you're allowed to develop a range of commercial and residential uses, but there are some specific guidelines to consider. Here are the general types of development permitted under BU-2 zoning:
1. Commercial Uses:
Retail businesses (e.g., shops, restaurants, cafes)
Offices (e.g., professional services, banks, medical offices)
Personal services (e.g., salons, dry cleaners, gyms)
Hotels, motels, or inns
Warehousing and distribution (with limitations)
Automotive businesses (e.g., car dealerships, service stations)
2. Residential Uses:
Multi-family residential buildings (e.g., apartment buildings, condominiums)
Mixed-use buildings (combining residential with commercial on lower floors)
3. Special Uses:
Daycare centers
Cultural facilities (e.g., museums, galleries)
Health-related facilities (e.g., clinics, outpatient care centers)
Restaurants and bars with liquor licenses
4. Accessory Uses:
Parking structures (either above or below ground)
Limited outdoor sales areas, depending on the specific location and use
Temporary structures for special events
Restrictions & Considerations:
Height Limits: You’ll be subject to height restrictions, depending on the area and proximity to residential zones. Typically, buildings can be up to 8 stories (though this can vary by location).
Setbacks: There may be requirements regarding the distance between your building and the property line, especially for residential uses.
Parking: Adequate parking spaces for residential and commercial uses must be provided.
Special Permits: For certain uses like drive-thru establishments or specific event spaces, you might need additional permits.
FOR SALE DETAILS
PRICE
$11,500,000 USD
PRICE/ACRE
$15,719,710/AC
PRICE/SF
$361 USD /SF
# OF LOTS
-
LAND DETAILS
PROPERTY TYPE
Land
PROPERTY SUBTYPE
Commercial
LAND PROPOSED USE
Commercial, Apartment Units, Apartment Units - Condo, Apartment Units - Dorms, Apartment Units - Senior, Apartment Units - Subsdzd
LAND ACRES
0.73 AC
LAND SF
31,867 SF
OFFSITE IMPROVEMENTS
-
ZONING
BU-2/BU-3
APN/PARCEL ID
30-4108-030-0050
ASK ABOUT THIS PROPERTY
Please correct the highlighted field(s).

786-245-1165
By clicking the button, you agree to Showcase's Terms of Use and Privacy Notice.
Please correct the highlighted field(s).

786-245-1165
By clicking the button, you agree to Showcase's Terms of Use and Privacy Notice.